Introduction
In recent years, cryptocurrency has emerged as a popular alternative to traditional banking. To provide some context, cryptocurrency refers to digital or virtual currency that employs cryptographic techniques for security and operates independently of a central bank. While traditional banking has a long history spanning centuries, cryptocurrency represents a relatively recent innovation that has gained substantial momentum over the past decade.
As of May 15th, 2023, the new idea has gained a lot of attention. Right now, all the cryptocurrencies together are worth about $2.3 trillion USD. The biggest one, Bitcoin, is worth around $1.1 trillion USD. There are thousands of different cryptocurrencies, and more keep popping up. People and businesses all over the world are starting to use cryptocurrencies as a way to pay for things.
Disrupting the Conventional Banking Landscape
Cryptocurrency has wrought significant disruption to the traditional banking sector. It has effectively challenged the established banking paradigm by providing an alternative avenue for conducting financial transactions. Consequently, there has been a notable redistribution of influence from traditional banks toward cryptocurrency exchanges.
Cryptocurrency exchanges empower users to engage in the buying and selling of digital currencies without the necessity of a conventional bank intermediary. This shift has enabled users to expedite and economize on fund transfers, given the circumvention of traditional banking processes. Furthermore, cryptocurrency exchanges offer heightened transparency. This is because of the meticulous recording of all transactions on a public ledger.
Escalated Competitive Dynamics
The ascent of cryptocurrency has ushered in heightened competition within the financial industry. Traditional banks no longer reign supreme as the sole choice for consumers seeking financial services. Cryptocurrency exchanges and other fintech enterprises have entered the arena, proffering innovative product suites and services.
This amplified competition has propelled traditional banks toward adaptation and innovation. In a bid to remain pertinent in a swiftly changing landscape, banks are allocating resources to enhance their technological infrastructure. For instance, certain banks are exploring the utility of blockchain technology, the foundational technology underpinning cryptocurrencies.
Navigating Regulatory Complexities
While cryptocurrency disrupts traditional banking, it simultaneously presents regulatory quandaries. Cryptocurrency operates independently of central banks, rendering it challenging for governments to exert regulatory control. As a result, concerns have arisen concerning issues such as money laundering and illicit activities.
Governments across the globe grapple with the formulation of comprehensive cryptocurrency regulations. Some nations have imposed outright bans on cryptocurrency, while others have instituted stringent regulatory frameworks. The absence of standardized regulations has generated market uncertainty, hampering the entry of traditional banks into the cryptocurrency sphere.
Security Apprehensions
Another dimension of cryptocurrency’s impact on traditional banking revolves around security apprehensions. Cryptocurrency transactions rely on cryptographic protocols, bolstering security but also introducing susceptibility to hacking.
Traditional banks, with their centuries-long existence, have established the best security measures to safeguard customer assets. Conversely, cryptocurrency exchanges, being relatively new, have yet to attain the same level of security maturity. Consequently, the cryptocurrency market has witnessed several high-profile exchange breaches, eroding consumer trust.
How Banks Can Embrace Cryptocurrency
To stay competitive, banks must welcome cryptocurrency as a useful tool rather than a threat. Cryptocurrency adoption can enhance financial services, and recent industry developments ease banks’ concerns about risks, highlighting potential benefits.
Custody Services: Banks can now provide secure crypto custody services approved by the OCC, ensuring customers’ crypto assets’ safety.
Facilitating Newcomers: Banks can create user-friendly tools to help new investors join the crypto world. Many inexperienced investors prefer storing crypto with trusted banks rather than unregulated entities.
AML/KYC Compliance: Banks can adhere to anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations when dealing with cryptocurrency transactions, reducing the risk of illegal activities.
Blockchain’s Role: Blockchain technology could streamline AML/KYC verifications across institutions, improving security and efficiency.
Enhanced Security: Banks can protect crypto holdings from theft or hacks, addressing security concerns.
Efficient Payments: Banks can leverage blockchain for faster and cheaper payment processing.
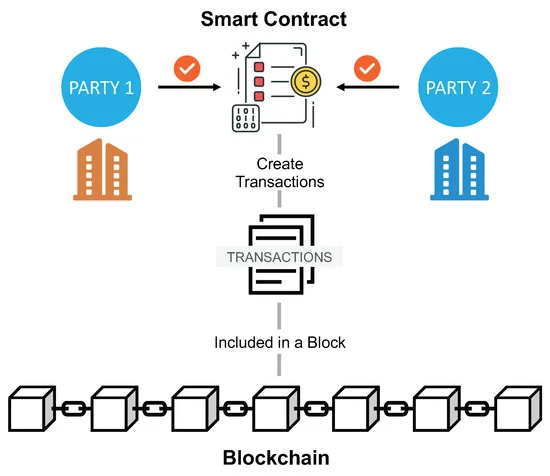
Smart Contracts: Banks can use smart contracts to facilitate various transactions, enhancing trust and reliability.
India’s Top Cryptocurrency-Friendly Banks
HDFC Bank: A major private-sector bank, HDFC, champions digital banking and allows customers to buy, sell, and store cryptocurrencies. They also provide educational resources on crypto.
ICICI Bank: Another leading private-sector bank, ICICI, offers crypto services and educational resources to help customers understand digital currencies.
Axis Bank: Actively exploring crypto potential, Axis Bank enables users to transact in cryptocurrencies and partners with Ripple for instant cross-border payments.
Yes Bank: At the forefront of digital banking, Yes Bank facilitates crypto transactions and collaborates with crypto exchanges for a wider asset range.
Kotak Mahindra Bank: Embracing cryptocurrencies, Kotak Mahindra lets customers engage with digital assets and partners with crypto exchanges for broader offerings.
IndusInd Bank: Recognizing crypto’s potential, IndusInd Bank supports crypto transactions and collaborates with crypto exchanges for an extended asset range.
Federal Bank: With a crypto-friendly approach, Federal Bank allows customers to deal with cryptocurrencies and partners with crypto exchanges for diverse digital assets.
IDFC First Bank: Exploring crypto’s potential, IDFC First Bank supports crypto transactions and collaborates with crypto exchanges for a broader asset range.
SBI: India’s largest public-sector bank, SBI, ventures into blockchain and explores digital asset use, although not offering direct crypto services yet.
Union Bank of India: A public-sector bank, Union Bank, supports crypto transactions and collaborates with crypto exchanges for a wider range of digital assets.
Pros of Crypto-Friendly Banks:
- Facilitated Transactions: Streamline buying, selling, and storing cryptocurrencies alongside traditional banking operations.
- Enhanced Security: Benefit from rigorous bank security measures, assuring the safety of crypto assets.
- Dedicated Support: Access specialized customer support for crypto-related concerns.
- Regulatory Compliance: Alignment with Reserve Bank of India regulations ensures adherence to crypto rules.
- Increased Adoption: Growing acceptance of cryptocurrencies fuels mainstream awareness and usage.
Cons of Crypto-Friendly Banks:
- Limited Availability: Few crypto-friendly banks can make finding a suitable option challenging.
- Higher Fees: Some banks impose elevated fees for crypto transactions, potentially increasing costs.
- Security Risks: Despite stringent measures, crypto usage may pose security threats like hacking.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Ongoing uncertainty regarding crypto regulations can hinder confidence.
- Limited Support: Varying levels of customer support may affect user assistance.
Conclusion
In summary, cryptocurrency has significantly changed traditional banking by offering a new way to do transactions and more competition. However, it has also created regulatory and security issues. Whether cryptocurrency can fully replace traditional banking is still uncertain.